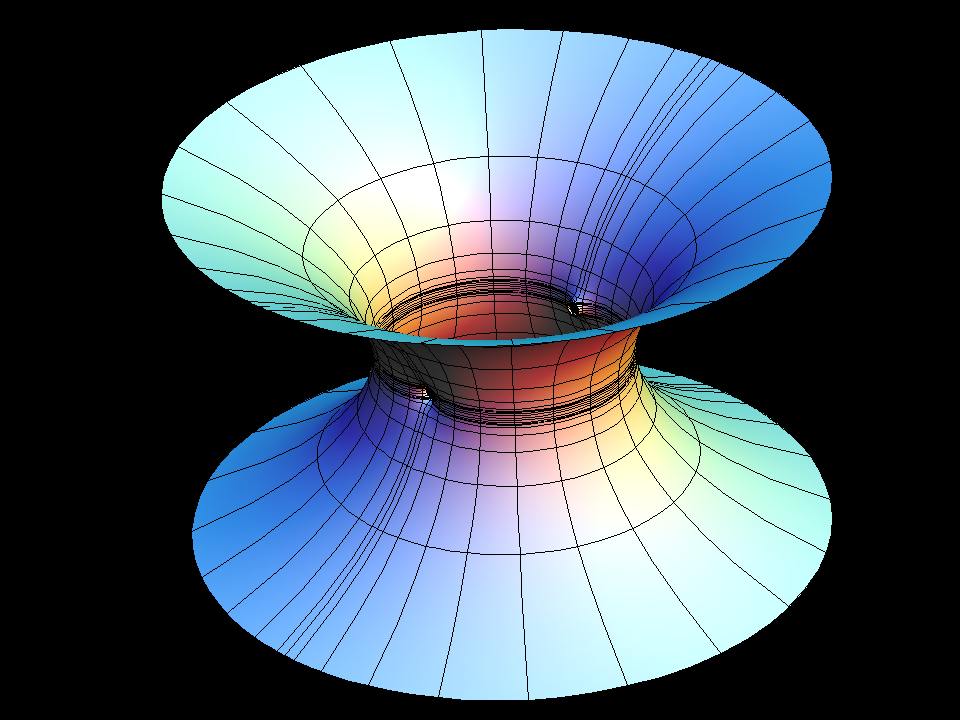

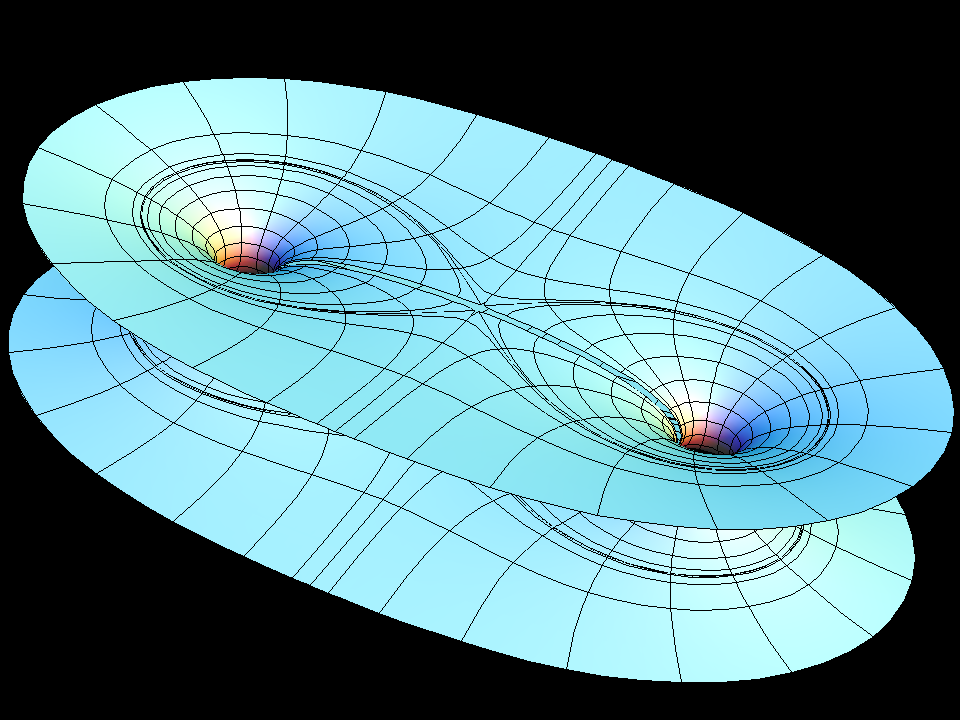
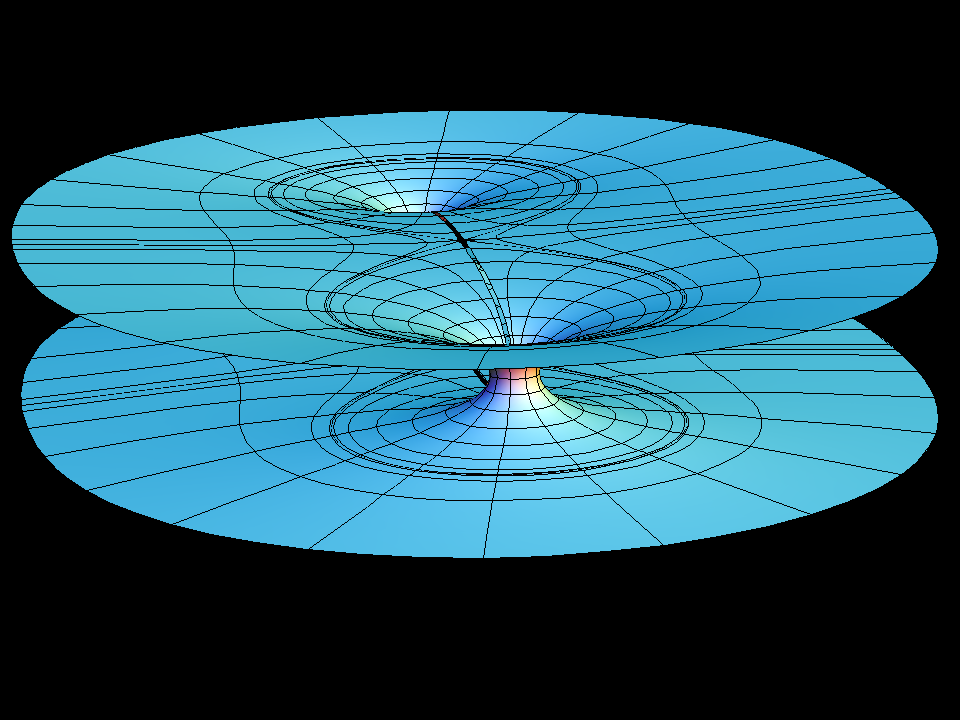
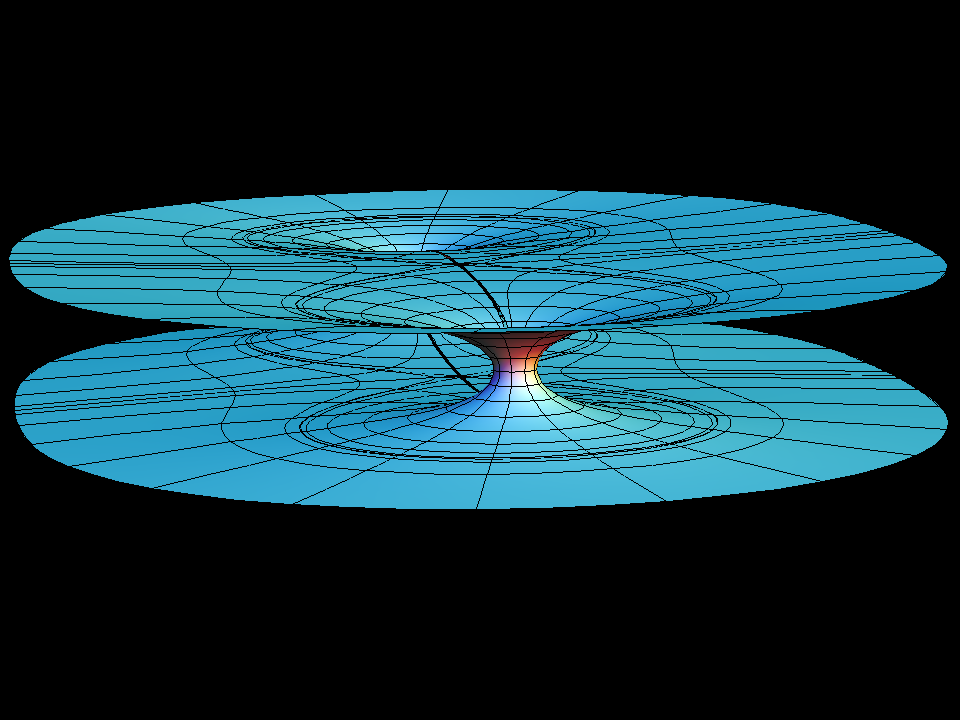
see Catenoid Fence
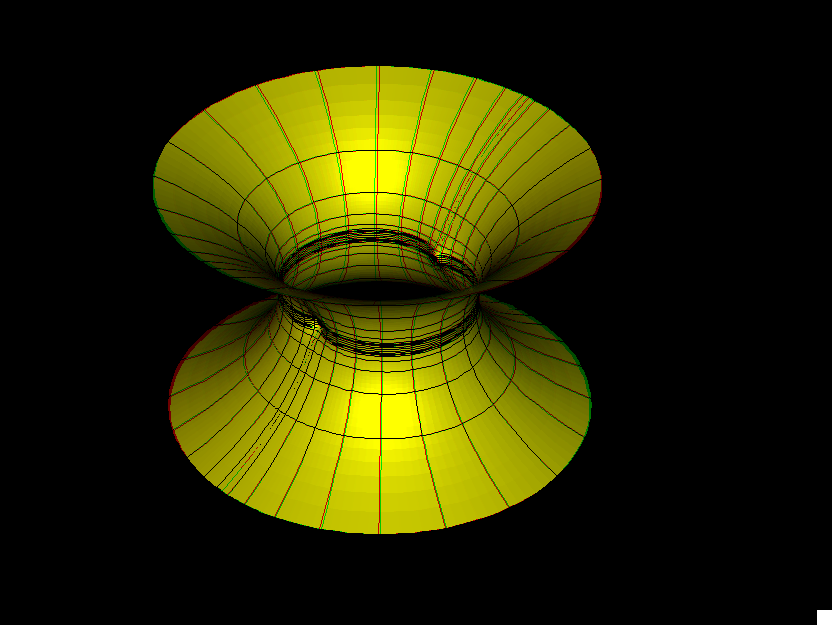
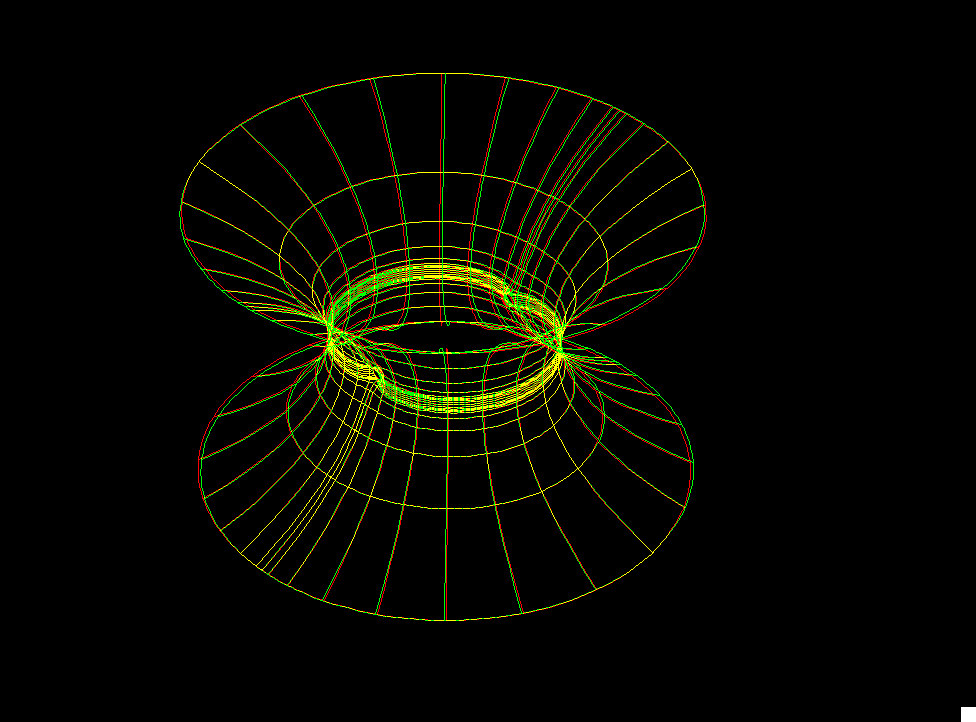
R. Schoen's characterization of the catenoid says: Any finite total curvature complete embedded minimal surface which has TWO ends, is the Catenoid.
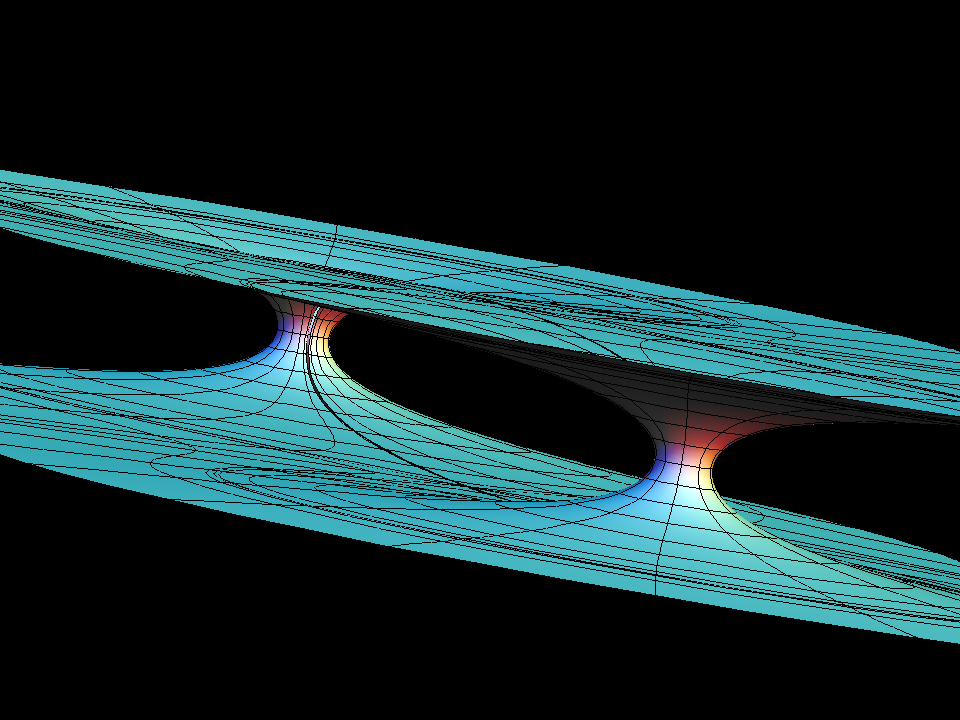
Our example shows what happens if one tries — in spite of Schoen's theorem — to add a handle to the catenoid. The fundamental piece is similar to that of the catenoid fence, except that the handle does not go outward to the neighbouring catenoid but goes inward to meet its other half. However a gap remains and as one tries to close it (by morphing with the modulus, aa, of the underlying rectangular Torus) the surface degenerates to look almost like two catenoids which move farther apart as one tries to close the gap. We try to show this with the suggested morphing; the deformation goes between rather extreme surfaces where one has to adjust how far one computes into the end and then also the size. The movie is still a bit jumpy.
For a discussion of techniques for creating minimal surfaces with various qualitative features by appropriate choices of Weierstrass data, see either [KWH], or pages 192--217 of [DHKW].