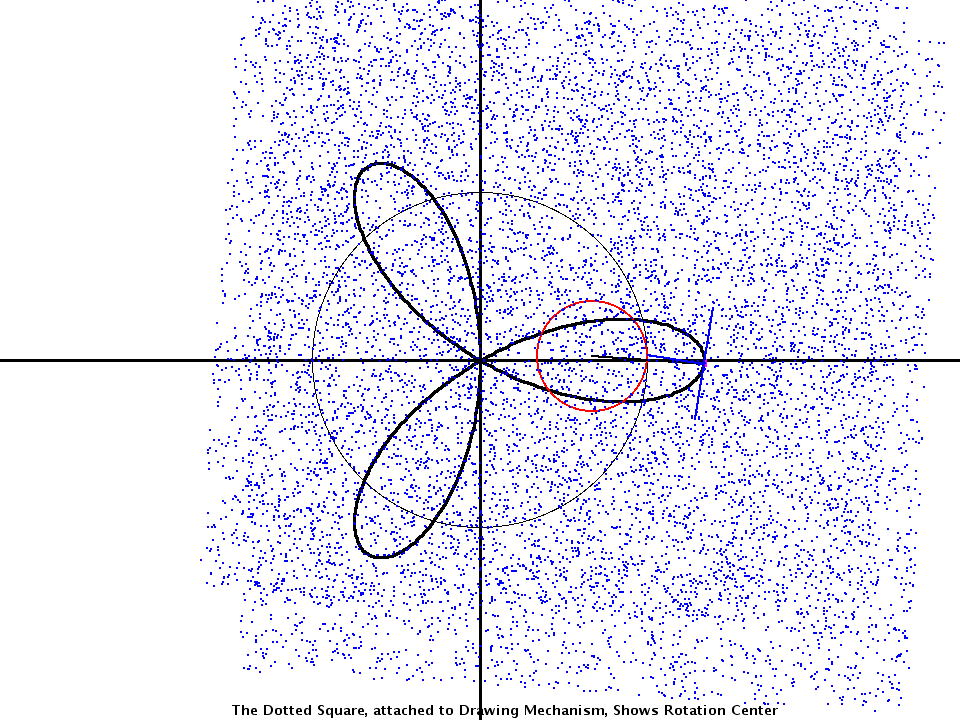
Epicycloids and Hypocycloids
The curves are defined by these equations:
c(t) = [ RR * cos(t), RR * sin(t) ] +
[ sticklength*cos(frequency*t),
sticklength*sin(frequency*t)];
The curve and ists tangents are obtained from a rolling construction.
If sticklength = RR/|frequency| (stick = 1), the curves are called epicycloids - which roll outside - and hypocycloids - which roll inside. For other sticklengths these curves are called epitrochoids resp. hypotrochoids.
c(t) = [ RR * cos(t), RR * sin(t) ] +
[ sticklength*cos(frequency*t),
sticklength*sin(frequency*t)];
The curve and ists tangents are obtained from a rolling construction.
If sticklength = RR/|frequency| (stick = 1), the curves are called epicycloids - which roll outside - and hypocycloids - which roll inside. For other sticklengths these curves are called epitrochoids resp. hypotrochoids.